Understanding Aviation Hot Spots: A Guide to Safety
Aviation safety is a critical priority, particularly at airports where complex operations create significant challenges. Therefore, among these challenges, Enhancing Aviation Safety Through Hot Spot Awareness emerge as key areas on airport movement zones that carry a high risk of collisions or runway incursions. Moreover, these locations demand heightened vigilance from pilots and drivers to prevent accidents. In this detailed guide, we explore what hot spots are, why they matter to aviation safety, and the strategies used to mitigate their risks. Additionally, we highlight how E3 Aviation supports pilots with essential training and resources. By relying on official aviation sources and real-world examples, we aim to deliver a comprehensive resource for aviation enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Defining Aviation Hot Spots and Their Significance
Hot spots are specific areas on an airport’s movement zones—such as taxiways, runways, and aprons—where there’s a documented or potential risk of collisions or runway incursions. For example, these areas often feature complex intersections, confusing layouts, or limited visibility, making them particularly hazardous. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) marks these aviation hot spots on airport diagrams to assist pilots and drivers in navigating safely. Moreover, understanding hot spots is vital because they directly contribute to runway incursions—serious safety incidents. According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway incursion is defined as ‘any occurrence at an aerodrome involving the incorrect presence of an aircraft, vehicle, or person on the protected area of a surface designated for the landing and take-off of aircraft’ (Hot Spots at Aerodromes | SKYbrary Aviation Safety). Consequently, such events can lead to catastrophic accidents, emphasizing the need for awareness and caution around hot spots.
Furthermore, the significance of hot spots stems from their reflection of design or operational challenges that standard measures like signage or lighting may not fully resolve. For instance, reduced visibility, intricate taxiway-runway intersections, and limitations in visual control rooms or surveillance systems can increase risks. Therefore, effective pre-flight planning and situational awareness are essential for pilots to manage these hazards.
Real-World Examples: Aviation Hot Spots in Action
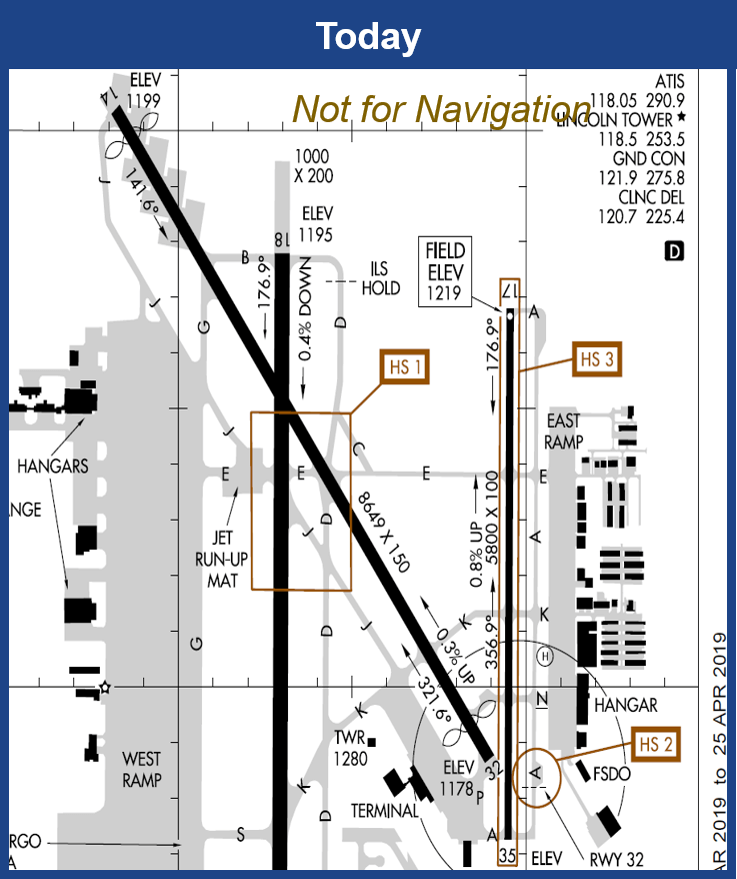
To illustrate, let’s examine Ft. Lauderdale Executive Airport (FXE), a busy general aviation hub with multiple identified hot spots. For example, pilots landing on Runway 9 might miss Taxiway Bravo and mistakenly turn onto Runway 13-31, risking conflicts with other aircraft. Similarly, at the southeast corner, pilots departing from the Charlie ramp may miss Taxiway Bravo and enter Runway 13-31 instead. Additionally, near the U.S. Customs Ramp, overlooking Taxiway Golf could lead pilots to cross the approach end of Runway 31, underscoring the need for precise navigation.
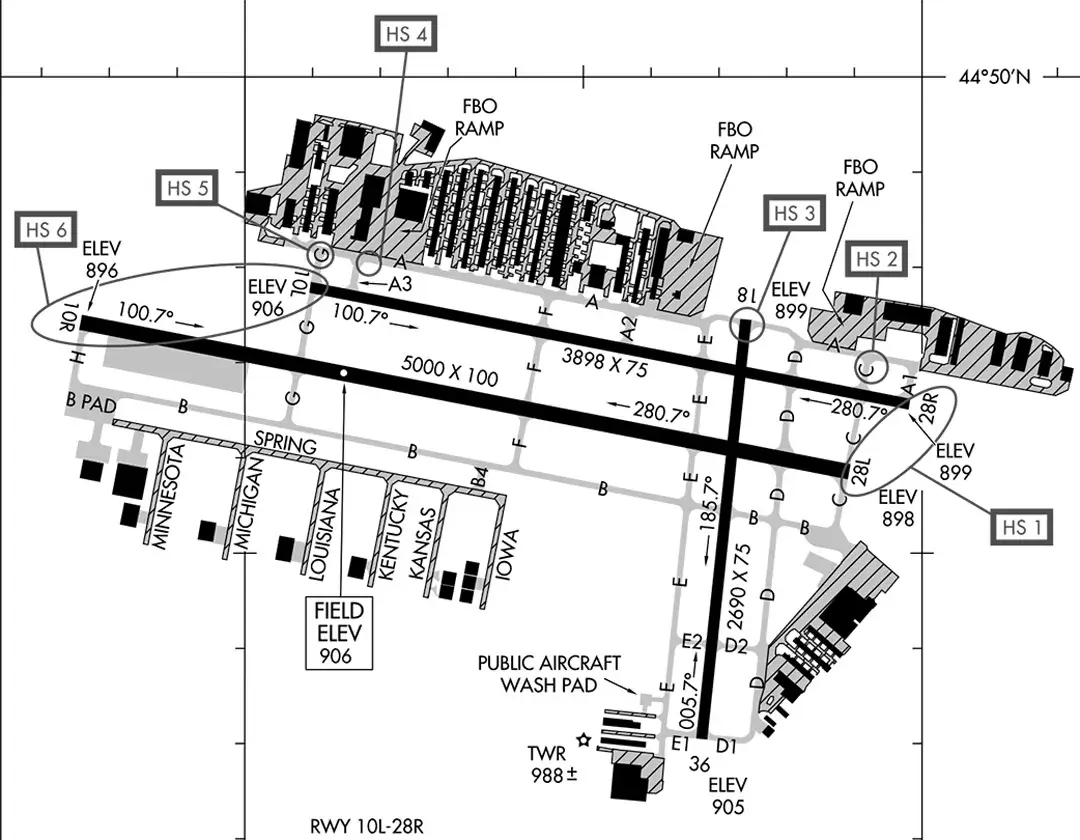
Meanwhile, Flying Cloud Airport (KFCM) in Minneapolis offers another example, Enhancing Aviation Safety Through Hot Spot Awareness with six hot spots due to the close proximity of runways and taxiways. Specifically, this setup increases confusion during low visibility or nighttime operations. For instance, the intersection of Runways 28L/28R and 10L/10R poses a risk of wrong-surface events, while areas near Runway 28R/10L are dangerously close to taxiways, heightening collision risks (FAA Safety Briefing Magazine). Likewise, smaller airports like Sugar Land Regional Airport (KSGR) face similar issues, with a hot spot at the intersection of Taxiway E and Taxiways A and A3, where short distances to Runway 17/35 elevate conflict potential.
Moreover, at larger airports like Los Angeles International (LAX), hot spots are prevalent due to high traffic and complex layouts. For example, the intersection of Taxiway B and Runway 24L/06R is a known hot spot where pilots must be extra cautious to avoid missing hold short lines.
Standardized Symbology: Enhancing Clarity for Hot Spots
To reduce pilot confusion, the FAA introduced standardized hot spot symbols on May 19, 2022, as outlined in their newsroom (FAA Hot Spot Standardized Symbology). Specifically, these symbols include:
| Symbol | Type | Description |
| Circle or Ellipse | Ground Movement Hot Spot | Marks areas with risks like hold short violations or complex taxiway layouts. |
| Cylinder | Wrong Surface Hot Spot | Indicates locations where aircraft might use the wrong surface for takeoff or landing. |
Additionally, these FAA hot spot symbols are integrated into airport diagrams within chart supplements and the Terminal Procedures Publication. Consequently, pilots can quickly recognize and interpret hot spots during pre-flight planning. Previously, inconsistent symbols like squares and rectangles caused confusion, but this standardization enhances safety through uniform recognition.
Old Symbology
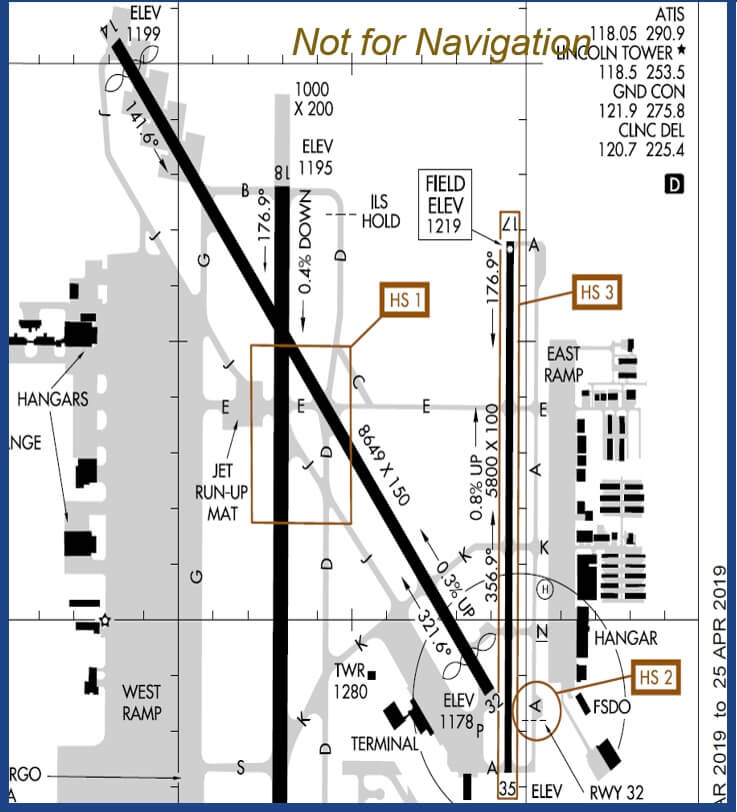
New Symbology
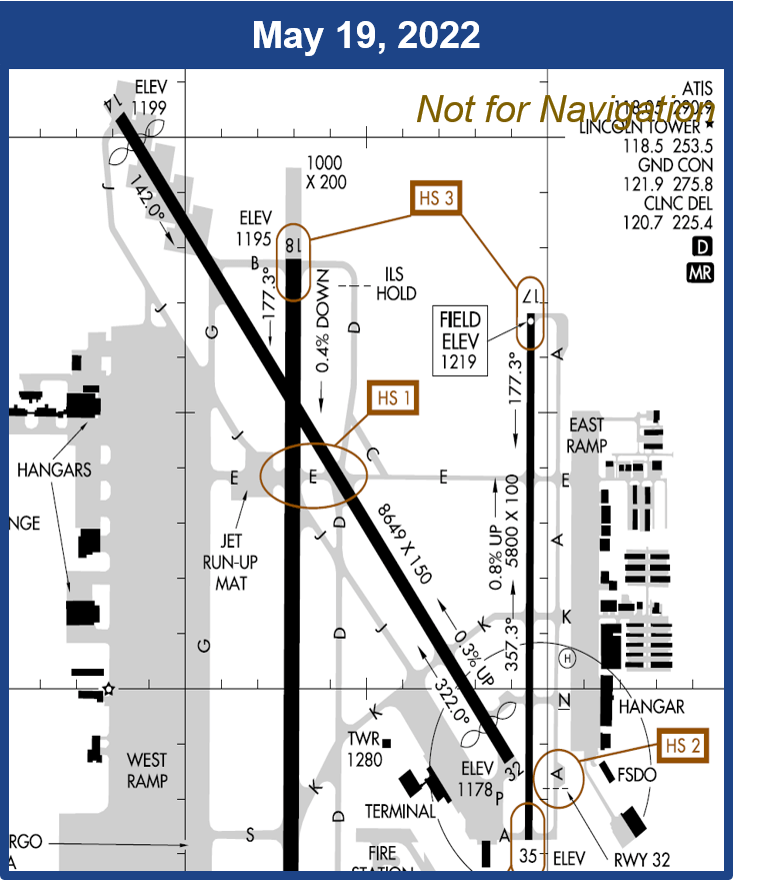
Mitigation Strategies: Reducing Risks at Hot Spots
Mitigating risks at aviation hot spots requires coordinated efforts from airports and pilots. Specifically, airports implement the following strategies:
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating pilots and operators about specific hot spots via resources like the Chart Supplement (FAA Hot Spots).
- Enhanced Visual Aids: Upgrading signage, markings, and lighting to clarify paths, as seen at KFCM (SKYbrary).
- Alternative Taxi Routes: Rerouting traffic to avoid high-risk zones, minimizing exposure to hot spots.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Building new taxiways or closing hazardous areas to simplify navigation, per ICAO guidelines (SKYbrary).
- Tech Solutions: Using CCTV or radar to monitor blind spots, enhancing runway incursion prevention (AOPA Airport Operations).
Meanwhile, pilots can adopt best practices to navigate hot spots safely. For example, studying airport diagram hot spots before taxiing, maintaining clear communication with air traffic control (ATC), and exercising caution near hot spots are critical steps. At FXE, pilots are advised to double-check taxi clearances and hold short lines, especially on Taxiway Foxtrot, where errors can lead to conflicts.
Enhancing Aviation Safety Through Hot Spot Awareness
E3 Aviation’s Role in Enhancing Pilot Safety
E3 Aviation plays a crucial role in improving pilot safety through comprehensive pilot safety training programs and community resources focused on hot spot awareness. Specifically, their initiatives ensure pilots stay informed about standardized symbols, mitigation strategies, and best practices for navigating complex airport environments. Moreover, by fostering a collaborative culture where pilots share insights and experiences, E3 Aviation strengthens the aviation community, empowering aviators to handle hot spots confidently.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Approach to Aviation Safety
Hot spots pose a significant challenge in aviation, but their risks can be managed through airport interventions, standardized tools, and pilot preparedness. For instance, examples from FXE, KFCM, KSGR, and LAX highlight the variety of hot spot scenarios, while the FAA’s standardized symbology and mitigation strategies provide actionable solutions. Additionally, E3 Aviation’s support ensures pilots are well-equipped to navigate these critical areas. Ultimately, by staying informed and vigilant, the aviation community can enhance safety, making every flight a step toward a safer sky.
For more E3 Aviation resources, be sure to visit: https://e3aviationassociation.com
Keywords: aviation hot spots, runway incursion, airport safety, pilot training, FAA symbols, runway incursion prevention, pilot safety training, FAA hot spot symbols, airport diagram hot spots, aviation safety strategies